Introducing: Lumar for GEO (Generative Engine Optimization).
We’re building the next generation of optimization tools.
For SEOs, marketers, and product managers, the question is no longer just how to rank in traditional search engines, but also how to maintain a strong share of voice in AI search — but the playbook for AI search and generative engine optimization is still being written.
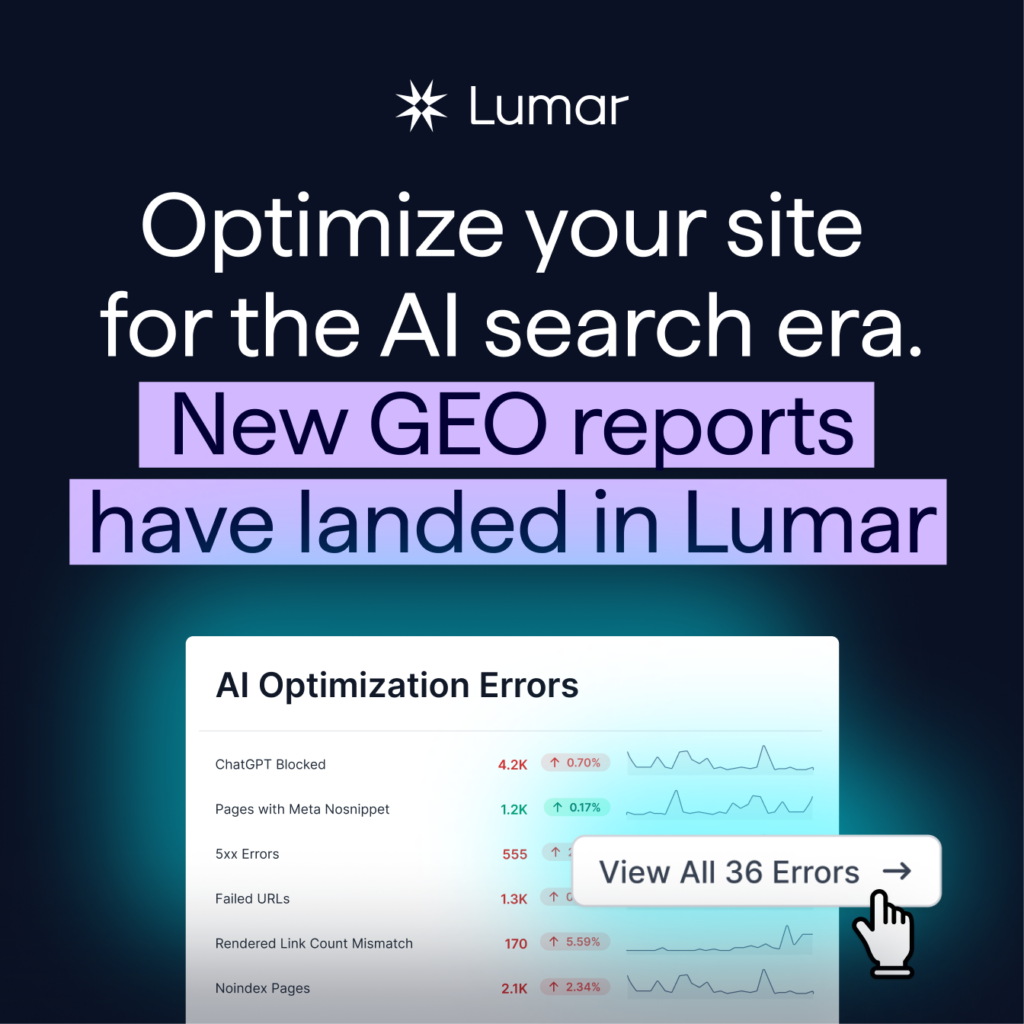
Today, we’re releasing new GEO dashboards in Lumar to help your brand show up in today’s AI search landscape. Lumar’s AI research and development team has spent months examining how AI engines work today, and what website optimizations can move the needle when it comes to getting your brand’s content included in AI responses and AI-powered search.
Lumar’s new GEO toolkit provides a data-driven view of your site’s performance against a new set of AI-focused metrics. This allows you to move from GEO guesswork to analysis, making informed decisions on what’s driving AI visibility for your brand — and where technical debt and content issues on your website may be creating roadblocks for your AI inclusion. Instead of chasing unverified best practices when it comes to AI visibility, Lumar’s GEO toolkit gives you the diagnostic reports to test hypotheses in this emerging field. Lumar is your technical audit platform for the age of generative AI.
TLDR? Get started with a Lumar GEO platform demo & see the tools in action yourself
Read on for the details about Lumar’s new GEO toolkit — or see the platform in action firsthand with your personalized Lumar GEO demo — simply fill out the form here to get started.
Discover why Lumar is the website optimization platform of choice for leading enterprise brands:

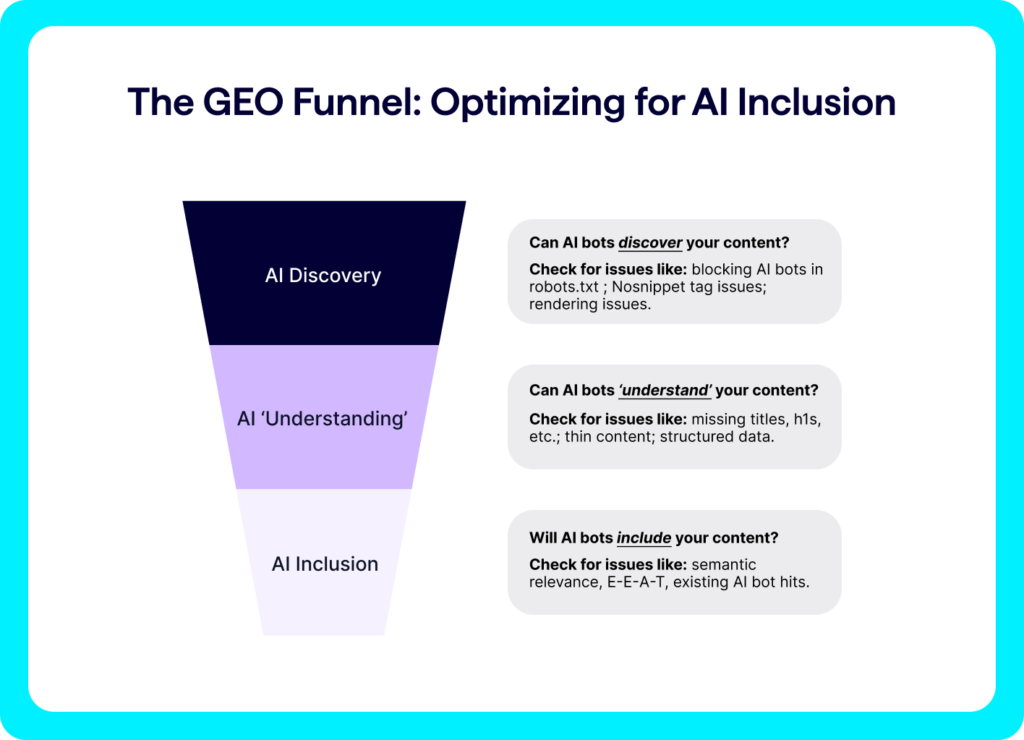
Your GEO workflow: Optimizing for AI discovery, understanding, & inclusion
For your brand’s content to appear in AI search and AI chatbots, you’ll need to ensure your website is optimized across three core areas:
- AI Discovery — Can your brand’s content be found, accessed, and rendered properly by AI bots?
- AI Understanding — Can AI systems “understand” and categorize your content appropriately?
- AI Inclusion — Is your brand’s content considered reputable and useful enough for inclusion in AI responses?
Explore Lumar’s new GEO toolkit
Lumar’s GEO tools are structured to mirror the full AI optimization journey so you can quickly see how your site performs at each stage, identify what’s holding you back, and take focused action to improve AI visibility for your brand.
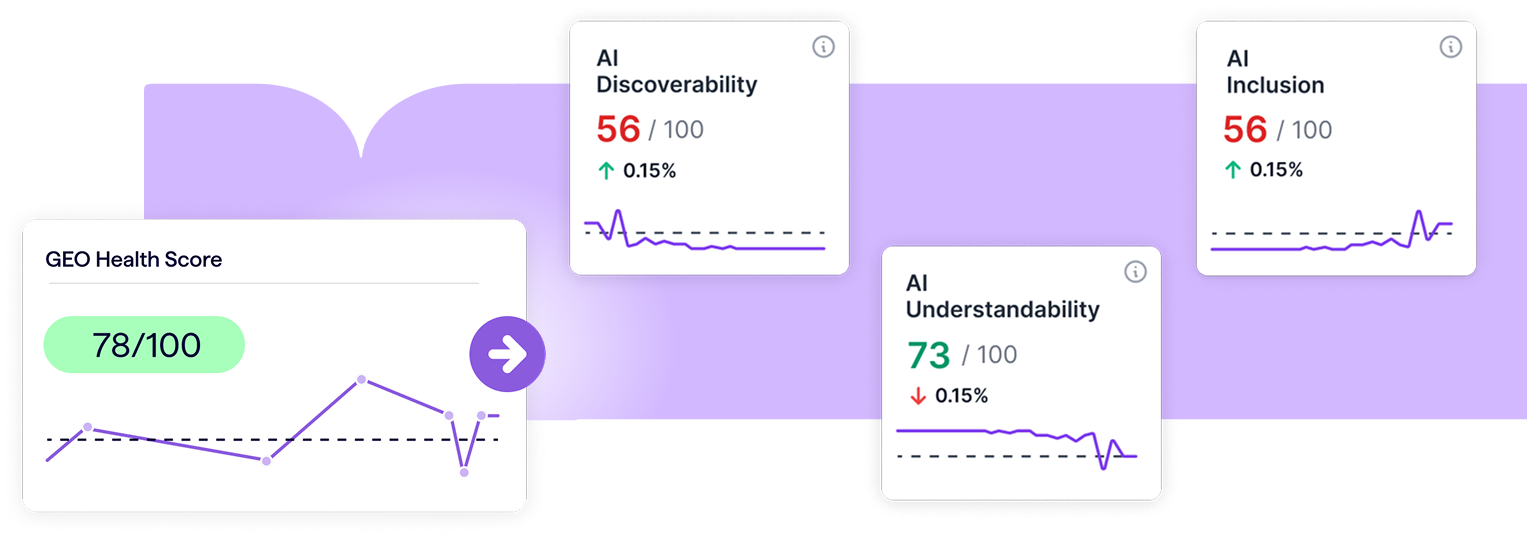
In the GEO Overview dashboard, you’ll get a high-level, at-a-glance, and easily shareable view of your site’s current AI optimization scores. From there, dig into 90+ reports across AI Discovery, AI Understanding, and AI Inclusion to pinpoint the exact areas where your site is succeeding — or falling behind — in its GEO efforts.
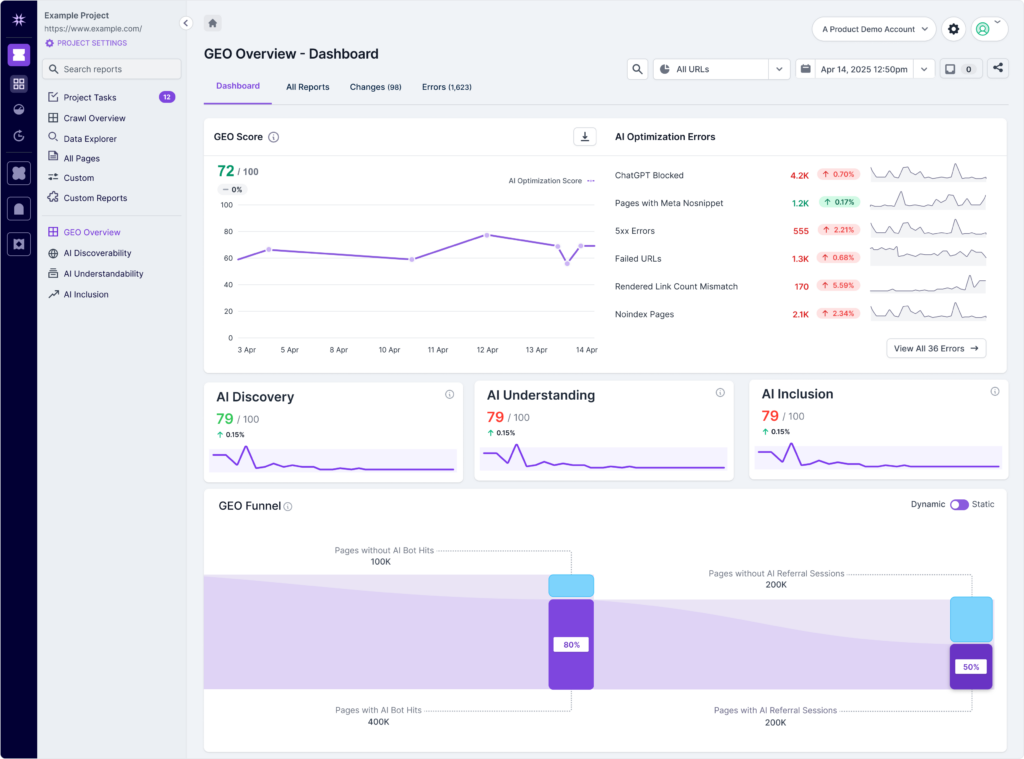
Lumar’s GEO reports are logically organized according to the GEO funnel workflow described above, helping you dive deep into the factors impacting each stage of the GEO funnel and prioritize your fixes to optimize effectively.
Now, let's dig into the new Lumar GEO tools, following the GEO funnel step by step...

Step 1: Optimize for AI Discovery
Lumar’s AI Discoverability reports help you optimize for the foundational stage of AI inclusion optimization: enabling AI bots to find (and access) your brand’s content.
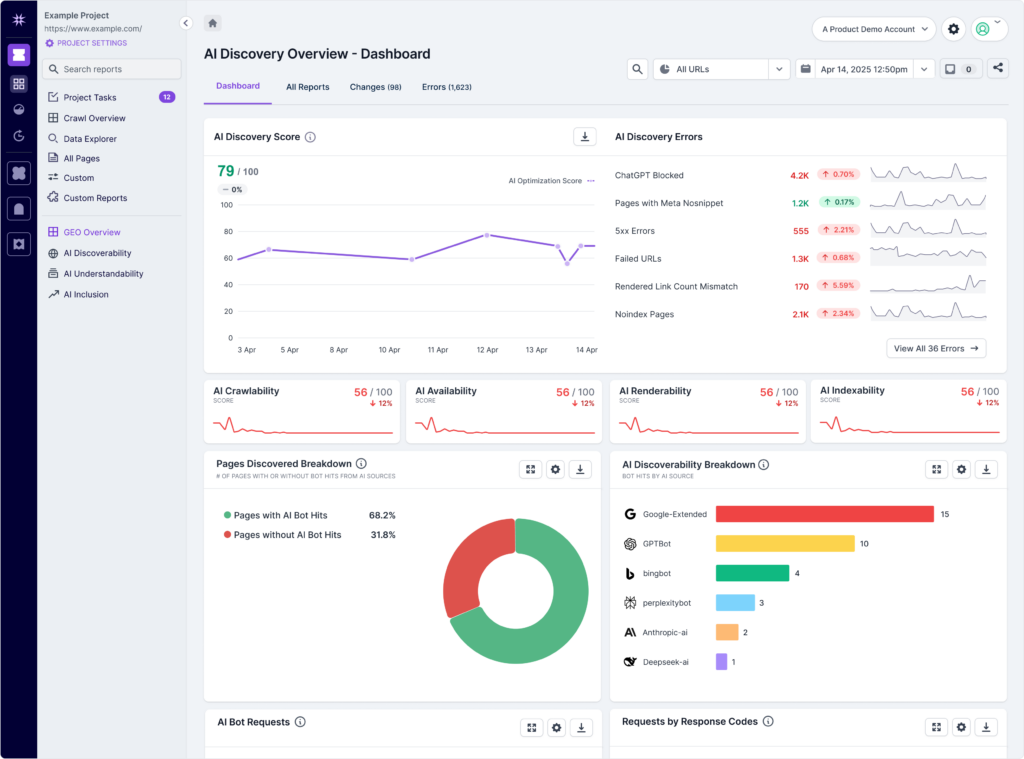
AI crawlability metrics
A critical first step in GEO is making sure AI systems can find and access your content. For your brand’s content to appear in AI-generated responses or AI-powered search results, it first needs to be technically crawlable and indexable. If AI and search engine bots can’t access your content, it won’t be included in the datasets or indexes these systems use to generate answers.
Are you blocking AI bots?
For GEO, it is fundamental to ensure that AI bots can access your website’s content. If pages on your site are blocking AI bots (e.g., via robots.txt), these systems cannot crawl and process the content, thereby preventing it from appearing in AI-generated summaries and directly hindering your AI search visibility.
If you want to appear in generative AI responses and AI search features, make sure your site isn’t unintentionally blocking important AI crawlers such as:
- GPTBot — If you want your brand or content to be cited in ChatGPT responses, you need to ensure you are not accidentally blocking OpenAI’s crawlers (like GPTBot) on your website.
- PerplexityBot — Perplexity is a major AI search engine. Blocking its crawler (PerplexityBot) from accessing your web pages can prevent your brand’s content from being included in its AI responses.
- Google-Extended — To appear in Google Gemini and other Google AI-related features, you should ensure your site is not blocking their AI-related crawlers (like Google-Extended).
- BingBot or BingPreview — Microsoft’s Bing search engine offers several controls available to limit inclusion in Bing Chat’s generative responses — check that your site is not accidentally set to block inclusion in Bing Chat, if you want your brand to appear there.
- CCBot — Common Crawl is a non-profit organization that continuously crawls the public web and freely provides its massive archives and datasets to the public. The data collected from these crawls is then made available in formats suitable for research and development. — Common Crawl is a foundational source of data for a significant number of AI models, particularly large language models (LLMs). It feeds many AI training datasets. Blocking the Common Crawl bot (CCBot) on your site limits AI models’ training exposure to your brand and content.
Blocked AI Bot Reports in Lumar GEO
( * = Coming soon )
| Lumar GEO Report: | What it Measures & Why it Matters for GEO: |
|---|---|
| AI Bot Blocked * | This Lumar report provides an overview of pages on your site that are blocking any known AI bots from accessing your content. |
| ChatGPT Blocked | This report shows pages on your site where the URL is blocked in robots.txt for the GPTBot or ChatGPT-User user-agent token. |
| Google AI Blocked | Shows pages where the URL is blocked in robots.txt for the Google-Extended user-agent token. |
| Perplexity Blocked * | Shows pages that are blocking Perplexity from accessing or using your brand’s content. |
| Bing AI Blocked | This report shows pages on your site that are specifically blocking Bing’s AI systems. |
| Common Crawl Blocked | This report shows you if your site is blocking Common Crawl bots from including your content in its datasets (which provide a significant amount of training data to LLMs). |
Nosnippet Issues for GEO
Are nosnippet tags preventing your content from appearing in AI responses?
In the era of GEO and AI search, the ability to control how your content is summarized is a powerful tool — or a critical issue if mismanaged.
The nosnippet directives (including the meta tag, X-Robots-Tag header, and data-nosnippet attribute) were originally designed to prevent search engines from creating rich text snippets in traditional search results.
Today, these same nosnippet directives are a direct signal to AI systems. By preventing a snippet from being generated, a nosnippet directive also prevents your content from being used as a direct input for AI-generated responses, AI Overviews, and other AI-powered SERP features.
The nosnippet meta tag is a crucial tool for GEO because Google has confirmed it prevents AI systems, including AI Overviews and AI Mode, from using a page's content to generate AI-powered snippets and responses.
Per Google Search Central, the nosnippet directive tells Google:
“Do not show a text snippet or video preview in the search results for this page. A static image thumbnail (if available) may still be visible, when it results in a better user experience. This applies to all forms of search results (at Google: web search, Google Images, Discover, AI Overviews, AI Mode) and will also prevent the content from being used as a direct input for AI Overviews and AI Mode.”
And per Google Search Central’s documentation on appearing in Google AI features:
“Technical requirements for appearing in AI features: To be eligible to be shown as a supporting link in AI Overviews or AI Mode, a page must be indexed and eligible to be shown in Google Search with a snippet, fulfilling the Search technical requirements.”
Lumar's Nosnippet Reports for GEO are designed to help you audit these directives, ensuring that your content is being used by AI systems exactly as intended, or conversely, that a misplaced tag isn't accidentally blocking your content from a valuable new source of visibility.
Nosnippet Reports in Lumar GEO
( * = Coming soon )
| Lumar GEO Report: | What it Measures & Why it Matters for GEO: |
|---|---|
| Pages with Meta Nosnippet * | This Lumar report provides a list of all pages with a Meta Nosnippet tag in place. |
| Pages with HTML Data-Nosnippet * | This report provides a list of all pages with an HTML data-nosnippet tag in place. — The data-nosnippet HTML attribute allows webmasters to mark specific parts of an HTML page so that Google does not use them as snippets. This provides more granular control than the nosnippet meta tag, which applies to the entire page. |
| Pages with Header Nosnippet * | This report tells you if there are X-Robots nosnippet tags on your site. — A header nosnippet tag (X-Robots-Tag: nosnippet [as an HTTP header response]) is similar in function to the other nosnippet tags. Its primary difference compared to the other types of nosnippet tags is its ability to apply nosnippet directives to non-HTML files, such as PDF documents, image files, video files, or other media, where you cannot embed HTML meta tags. It can also be used for HTML pages, especially if you want to manage these directives server-side for multiple pages or an entire site, without modifying individual HTML files. ) |
AI availability metrics
Before AI bots can crawl and parse your pages, the page must first be available for the bots to access.
To enable your website’s content to be discovered and cited in AI-generated answers, make sure none of your target pages return availability errors such as client-side 4xx errors (like 404 errors) or server-side 5xx errors. Both traditional search and AI bots cannot crawl pages that are unavailable, effectively excluding them from being referenced by generative models.
Availability Reports in Lumar GEO
| Lumar GEO Report: | What it Measures & Why it Matters for GEO: |
|---|---|
| Broken Pages (4xx Errors) | This report shows you broken pages on your website that are returning 4xx errors (like 404 errors). These URLs may have returned a working page at some point in the past or never served a working page at any point. |
| 5xx Errors | This report shows you broken pages on your website that are returning server-side 5xx errors. — URLs that return any HTTP status code in the range 500 to 599 (such as a 503) are often caused by a temporary server performance problem or a permanent issue where the server is unable to generate a working page from the URL |
| Failed URLs | Get a full picture of URLs on your site that are failing for any reason. This report shows URLs that were crawled by Lumar but did not return a response within our crawler’s timeout period of 9 seconds. This may be a temporary issue due to poor server performance or a permanent issue. |
| Redirect Loops | This report shows any pages on your website that have redirect loops in place. A redirect loop occurs when a URL redirects to another URL that eventually redirects back to the original page, creating an endless cycle that prevents the page from loading. This traps crawler bots, making the content inaccessible. |
| Redirect Chains | This report shows any pages on your website that have a redirect chain in place (URLs that redirect to another URL, which is also a redirect, resulting in a redirect chain). — A redirect chain is a linear sequence of two or more redirects that eventually leads to a final, successful destination page. While it is not an infinite cycle like a redirect loop, it is a less-than-ideal path for bots/crawlers that can waste crawl budget, create a slower user experience, and potentially delay indexing because it takes additional time for search engines to crawl. |
| JavaScript Redirects | This report shows all pages that redirect to another URL using JavaScript. — JavaScript redirects require bots to render the page before following the redirect, which consumes crawl/render budget and could lead to delays or missed execution. This makes them less reliable than server‑side redirects, especially at scale and with AI platforms that struggle with JavaScript rendering. |
| Internal Redirects Found in Web Crawl | This report shows all URLs that redirect to another URL with a hostname that is considered internal, potentially creating inefficient crawl paths for bots. |
AI rendering issues
What an AI bot "sees" is not always what a human sees — and may not even be what traditional search bots see. Content discrepancies between the raw HTML and the rendered page, which is processed after JavaScript is executed, can lead to a critical "content blind spot" for AI systems.
As Matt G. Southern reports in Search Engine Journal, while Googlebot is highly capable of rendering JavaScript, many other AI crawlers are not as advanced and rely on the static HTML:
“Traditional search crawlers like Googlebot can read JavaScript and process changes made to a webpage after it loads … In contrast, many AI crawlers can’t read JavaScript and only see the raw HTML from the server. As a result, they miss dynamically added content…”
This creates a new layer of technical GEO to manage. If any of your key content — the headings, paragraphs, and data that provide content authority — is only loaded via JavaScript, your most valuable information may be invisible to AI platforms.
The challenge for SEOs today is to ensure that a website's technical foundation is robust enough for all crawler bots, not just Google's.
Lumar’s AI Renderability reports are designed to help you diagnose and fix these JavaScript rendering issues, ensuring your content is seen and understood by the full spectrum of crawlers and AI bots.
AI Renderability Reports in Lumar GEO
| Lumar GEO Report: | What it Measures & Why it Matters for GEO: |
|---|---|
| Rendered Link Count Mismatch | This report shows all the pages on your site with a difference between the number of links found in the rendered DOM and the raw HTML source. — While modern search engines like Google can render JavaScript to find these links, many current AI systems struggle with JavaScript rendering. If a link to a high-value page is only found after rendering, a less-capable AI bot may not discover that content. |
| Rendered Canonical Link Mismatch | This report shows mismatches and inconsistencies in canonical tags and canonical links on your site. It shows pages with canonical tag URLs in the rendered HTML which do not match the canonical tag URL found in the static HTML. — Canonical tag inconsistencies can confuse bots about which content version to reference. For AI platforms to reliably cite your most important content, it is crucial to ensure that canonical tags are consistent across all versions of a page, including both the raw and rendered HTML. A mismatch in canonical links creates a conflicting signal for bots, which can lead to indexing errors or an AI platform citing a non-preferred version of your content. |
AI indexability metrics
Website indexability issues (such as pages being non-indexable via robots.txt, incorrect use of canonical tags, or using the unavailable_after directive) don’t just impact your traditional SEO and SERP results — they also have a knock-on impact on AI search results and AI-generated answers.
As Barry Schwartz explains in Search Engine Land, “To show in Google AI Mode & AI Overviews, your page must be indexed.”
ChatGPT & Bing’s search index
If, previously, you were primarily concerned only with getting your content indexed by Google, it may be time to expand your scope here for GEO because ChatGPT’s search function appears to rely heavily on Bing’s search index.
Per OpenAI’s announcement about ChatGPT Search:
“ChatGPT search leverages third-party search providers, as well as content provided directly by our partners, to provide the information users are looking for.”
And as Danny Goodwin writes in SEL, “One of those third-party search providers is Microsoft Bing. Based on its ChatGPT search help document, OpenAI is sharing search query and location data with Microsoft.”
Indexability Reports in Lumar GEO
| Lumar GEO Report: | What it Measures & Why it Matters for GEO: |
|---|---|
| Non-Indexable Pages | This report shows pages on your site that are non-indexable for any reason (ie, pages that return a 200 status but are prevented from being indexed via a noindex or canonical tag URL that doesn’t match the page’s URL). — To ensure your content is eligible for inclusion in generative AI responses and AI-powered search features, your pages should be indexable. Pages that are blocked from a search engine’s index are effectively invisible to many AI systems, which rely on these traditional search indices as a foundational source of information. |
| Canonicalized Pages | This report identifies all URLs on your website that contain a canonical tag pointing to a different URL. (In other words, these are pages that are designated as non-canonical or duplicate.) — A canonical tag is a direct hint to search bots to consolidate ranking signals and crawl budget to a single preferred URL. Mismanaging canonicals on your website can cause a wide range of issues that affect both traditional SEO and a site’s visibility in AI-powered search. |
| Noindex Pages | This report shows you all pages marked noindex. — A noindex directive tells bots not to include a page in the search index. In GEO, this could prevent your content from being surfaced, cited, or used by AI systems that rely on indexed material. Unintentional noindex tags can block high-value content from both traditional search and AI visibility. |
| Disallowed Pages | This report shows you all pages with a disallow directive in place. — Disallowing a page means you’re telling bots not to crawl it, which is done in the robots.txt file of your site. If important content is blocked, or ‘disallowed’, in your robots.txt file, crawlers—including some AI-related bots—cannot access it to understand or index it. Blocking should be used only for content you explicitly want excluded. |
| Unavailable_After Scheduled Pages | This report shows pages that are scheduled to become unavailable to bots after a specified date. — Future unavailability of a page may impact long-term AI content freshness evaluations. |
| Unavailable_After Non-Indexable Pages | This report shows pages that are both unavailable after a certain date and non-indexable. — Expired content is less likely to be referenced by AI systems in current responses. |

Step 2: Optimize for AI ‘Understanding’
Once you know that AI systems can access and render your site correctly — and that the search indices AI systems rely on can index it — you’ll want to ensure that AI systems can properly ‘understand’ and categorize your content within their vector embedding databases.
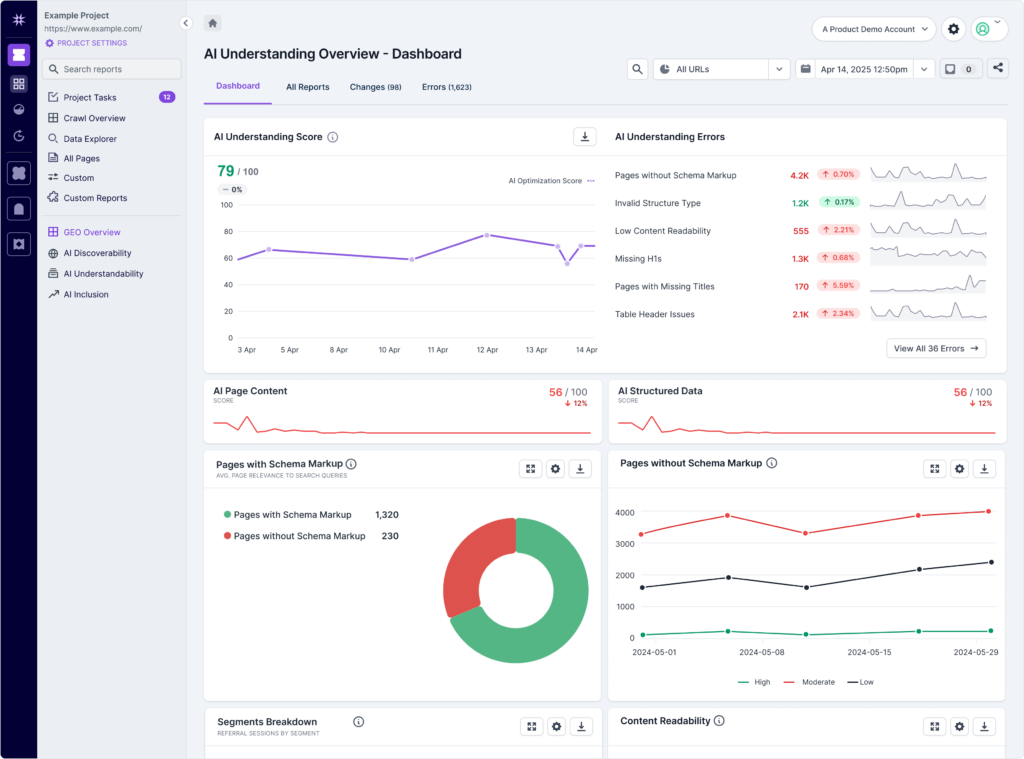
Lumar’s Page Content and Structured Data reports help you optimize your site’s content for AI understanding.
Page content metrics for GEO
Content structure issues like missing titles, missing H1s, missing meta descriptions, or large HTML size may impact a page's likelihood of being cited in generative AI responses and AI search platforms.
Content that is well-organized with appropriate use of title, h1, h2, etc. tags may also make it easier for AI systems to parse the information in your brand’s content (even though they are still capable of ‘understanding’ unstructured content).
Furthermore, there is likely an additional indirect impact here, caused by hindering the content's visibility within traditional search engine indexes, which AI search platforms and AI-powered SERP features then leverage in their generated responses.
As Matt G. Southern writes in SEJ: “The data shows a clear pattern: if you rank #1 on Google, you have a 1-in-4 chance of appearing in AI search results. Lower rankings result in lower chances.”
Page Content Reports in Lumar GEO
| Lumar GEO Report: | What it Measures & Why it Matters for GEO: |
|---|---|
| Missing Titles | This report shows pages on your site that are missing title tags. — The title tag is a primary signal that tells both users and bots what a page is about. Without it, bots must guess at the content’s topic, which can lead to miscategorization or a failure to recognize the page’s relevance for a specific query. |
| Short Titles | This report shows pages on your site have short title tags. — A short title tag often fails to provide sufficient context for bots, which can hinder an AI’s ability to accurately categorize your content. AI platforms are designed to provide authoritative and comprehensive answers, and they rely on clear on-page signals to identify the most relevant sources. |
| Missing H1 Tags | This report shows pages on your site that are missing H1 tags. — The H1 tag is the main heading on a page and a critical signal of content hierarchy. A missing H1 makes it more difficult for bots to identify the primary topic of the page, as it has lost a key structural and semantic cue. |
| Missing Descriptions | This report shows pages on your site that have short meta descriptions. |
| Short Descriptions | This report shows pages that are scheduled to become unavailable to bots after a specified date. — Future unavailability of a page may impact long-term AI content freshness evaluations. |
| Thin Pages | This report shows thin pages on your site (pages without very much content). — Pages with thin content provide limited value for AI training and response generation. |
| Max Content Size | This report shows pages on your site that have large content files. — Very large content may be truncated by AI systems with token limits. |
| Max HTML Size | This report shows pages on your site that have large HTML file size. — Large HTML files may impact bot crawling efficiency. |
| Rendered Word Count Mismatch | This report shows occurrences where the amount of visible text on a web page changes after a browser executes JavaScript, ie, pages with a word count difference between the static HTML and the rendered HTML. A rendered word count mismatch implies that a significant portion of your content is not readily accessible to crawler bots. As discussed above, AI bots rely heavily on raw HTML (rather than rendered content) when accessing content. |
Structured data for GEO
How structured data may impact AI visibility
While the core training of large language models (LLMs) used in AI bots primarily relies on vast quantities of unstructured data and text, many AI-powered search features (like Google's AI Overviews) that synthesize information from existing search engine indices may also indirectly benefit from structured data. This is because structured data helps traditional search engines better understand, categorize, and surface relevant content, which in turn can improve the chances of that content being selected and leveraged by the AI for its generative responses.
Large Language Models (LLMs) are trained on massive datasets of text; predominantly unstructured human language (books, articles, web pages). Most AI systems’ "understanding" of context primarily comes from patterns in natural language, not from directly parsing and interpreting schema.org markup in the same way a search engine's indexing system does.
But AI-powered search features from Google (like AI Overviews) and Microsoft (Copilot) do not re-crawl the web independently for every query. Instead, they leverage the vast, continuously updated indices of their respective search engines (Google Search Index, Bing Search Index). And structured data plays a crucial role in how today's search engines understand, organize, and retrieve information from the web.
Copilot's knowledge sources documentation, for example, indicates a direct reliance on the Bing search index:
"When turned on, Web Search triggers when a user's question might benefit from information on the web. It searches all public websites indexed by Bing."
And remember that Google Search Central documentation we mentioned previously?
“Technical requirements for appearing in AI features:
To be eligible to be shown as a supporting link in AI Overviews or AI Mode, a page must be indexed and eligible to be shown in Google Search with a snippet, fulfilling the Search technical requirements. There are no additional technical requirements.”
If structured data helps enable traditional SERP snippets and some LLMs and AI search features rely on traditional search engine indices for up-to-date information, then having proper structured data in place may also help your content appear in these AI-powered search features.
In short, while AI itself may not "read" structured data in a semantic way during its core training, structured data is vital for how search engines ingest, understand, and organize information. Since AI platforms and AI SERP features rely on these organized search indexes for the most current information, robust structured data implementation on your website may improve the chances of your content being considered relevant and chosen as a source for AI-generated responses.
A further consideration on AI and structured data comes from Jarno van Driel's interview on the Search With Candour podcast.
When asked, “With the growth of … natural language processing … do you think that shifts how important structured data is going forward?” he responded:
“The question is, is it financially viable? … The big advantage of structured data — any structured data set, it doesn’t necessarily have to be JSON-LD — the big advantage of those is that they really require little compute to be turned into something useful. And the biggest issue with all those LLMs, even the next generation five or ten years from now, is that it will cost a lot more compute to analyze unstructured content than to digest a piece of structured content. So even if meaning or understanding are not involved, it’s just a matter of money. It’s cheaper for any party to deal with structured data than to turn unstructured data into structured data to be able to use it. So that’s really the biggest benefit; it’s just a cost-efficient way for those parties to do something with data. Knowledge graphs and those kinds of repositories wouldn’t function without those large [structured] datasets.”
Structured Data Reports in Lumar GEO
| Lumar GEO Report: | What it Measures & Why it Matters for GEO: |
|---|---|
| Pages with Schema Markup / Structured Data | This report shows all pages on your website that have schema markup / structured data in place. |
| Pages without Schema Markup / Structured Data | This report shows all pages on your website that do not have schema markup / structured data in place, highlighting missed opportunities for content optimization. Content without structured data forces bots and search engine systems to rely on their own interpretation of the page’s natural language, which can lead to miscategorization or an incomplete understanding. While a page can still be indexed by search engines without structured data in place, it loses the competitive advantage of providing clear, machine-readable signals that help search systems parse and categorize content accurately and effectively. |
| Product Structured Data Pages | Our Product structured data reports show you pages that have Product schema in place, and which pages have valid or invalid structured data in this category. — Product schema enables bots and search engines to better understand and present details like price, availability, and reviews—key for e-commerce visibility. Per Google Search Central’s article on Product structured data: “When you add structured data to your product pages, your product information can appear in richer ways in Google Search results (including Google Images and Google Lens).” |
| Event Structured Data Pages | This report shows you pages that have Event structured data in place. |
| News Article Structured Data Pages | Shows you pages on your site with News Article structured data in place — and which pages have valid or invalid structured data in this category. NewsArticle schema signals that your content is timely, journalistic, and relevant for news-based queries—important for bots that prioritize trustworthy and recent information. |
| Breadcrumb Structured Data Pages | This report shows you pages that have Breadcrumb structured data in place. Breadcrumb schema gives bots clear information about a page’s place in your site hierarchy. This helps contextualize and categorize your content. |
| FAQ Structured Data Pages | This report shows you pages that have FAQ structured data in place. — FAQ schema can help bots explicitly pair questions with their answers in your content. (Note, per GSC: “FAQ rich results are only available for well-known, authoritative websites that are government-focused or health-focused.”) |
| How-To Structured Data Pages | This report shows you pages that have How-To structured data in place. HowTo schema breaks down procedural content into clearly defined steps, which bots and search engine crawlers can easily interpret and present in step-by-step formats. |
| Recipe Structured Data Pages | This report shows you pages that have Recipe structured data in place. — Recipe schema allows bots to extract ingredients, cooking steps, and nutritional info for your recipe-related content. |
| Video Object Structured Data Pages | This report shows you pages that have VideoObject structured data in place. Per GSC documentation on Video schema: “While Google tries to automatically understand details about your video, you can influence the information that’s shown in video results, such as the description, thumbnail URL, upload date, and duration, by marking up your video with VideoObject. Adding video structured data to your watch pages can also make it easier for Google to find your video. Videos can appear in several different places on Google, including the main search results page, Video mode, Google Images, and Google Discover." |
| QA Structured Data Pages | This report shows you pages that have QA page structured data in place. — QAPage schema helps bots match user questions with community-sourced answers. |
| Review Structured Data Pages | This report shows you pages that have Review structured data in place. — Review schema provides structured sentiment data about products, services, or businesses, which bots can incorporate into recommendations, summaries, and rankings. |

Step 3: Optimize for AI Inclusion
Even if AI bots — and the broader search engines many of them rely on for timely content inclusion — can find, access, and ‘understand’ your content, there’s no guarantee that your brand’s messages will be cited or linked to by AI platforms. So, what might help your content appear?
Because AI platforms want to avoid the reputational damage caused by AI ‘hallucinations’ and misinformation served in LLM responses, it makes sense that these AI systems also want to prioritize authoritative, trustworthy content — sound familiar? Our EEAT reports help you assess which content on your site is giving off signals that position your site and brand as experienced, expert, authoritative, and trustworthy.
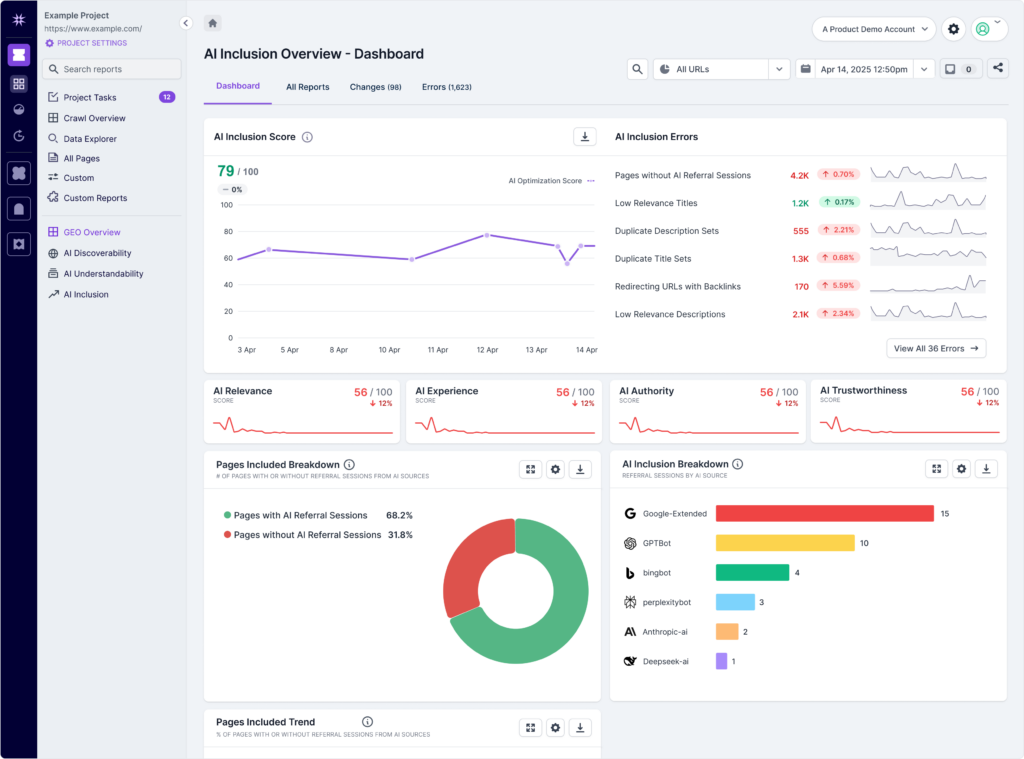
See which pages are already getting hit by AI bots
Lumar’s AI Bot Behavior reports can help you assess which pages on your site are currently getting AI hits — and which aren’t — so you can analyze what’s working for GEO.
AI Bot Behavior Reports in Lumar GEO
( * = Coming soon )
| Lumar GEO Report: | What it Measures & Why it Matters for GEO: |
|---|---|
| Pages With AI Referral Sessions * | This report is a positive indicator for GEO. It shows which pages on your website have been successfully accessed by any of the known AI bots. |
| Pages Without AI Referral Sessions * | This report shows pages on your website that have not been accessed by any AI bots. — This report is a crucial diagnostic tool for uncovering potential roadblocks to your content’s AI visibility. A lack of AI bot hits on a given page can signal a number of critical issues, such as it being blocked in robots.txt. If AI bots cannot find or access your content, it won’t be included in any generative response. This report helps you pinpoint and prioritize pages on your site that are known to be invisible or ignored by AI platforms. |
| Pages with GPTBot Hits * | This report shows pages that have been accessed specifically by ChatGPT’s AI bot. |
| Pages with Anthropic-ai Bot Hits * | This report shows pages that have been accessed specifically by Anthropic’s AI bot. |
| Pages with Google-Extended Bot Hits * | This report shows pages that have been accessed specifically by Google’s AI-related bot. |
| Pages with Bingbot Bot Hits * | This report shows pages that have been accessed specifically by Bing’s bot. (Note: It appears ChatGPT also makes use of Bing’s search index, so getting hits from Bingbot may also help with ChatGPT inclusion.) |
| Pages with PerplexityBot Bot Hits * | This report shows pages that have been accessed specifically by Peplexity’s AI bot. |
AI Authority & E-E-A-T for GEO
Beyond merely requiring relevance between content and a user’s query, AI platforms also prioritize high-quality, authoritative, and trustworthy sources to ensure the accuracy and reliability of their generated responses. Content that demonstrates expertise, experience, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness (E-E-A-T, in Google’s terms) is more likely to be selected.
Additionally, Google’s AI Overviews draw from the same traditional search ranking systems that prioritize E-E-A-T. If content is deemed “helpful” and demonstrates strong E-E-A-T for traditional search, it is probably more likely to also be considered a valuable source for AI summarization.
When it comes to other AI tools like those in Microsoft’s Bing, we also have clues that these systems are being developed to prioritize trustworthy content. In Microsoft’s “Responsible AI” document, it underscores Microsoft’s commitment to “Fairness,” “Reliability & Safety,” and “Transparency” in its AI systems. For Bing’s Copilot to be reliable, safe, and transparent, the sources it uses for information should be demonstrably accurate and trustworthy.
Likewise, in Perplexity’s help articles, it states that “When you ask Perplexity a question, it uses advanced AI to search the internet in real-time, gathering insights from top-tier sources.” — Again, content quality and E-E-A-T signals are at work here.
These AI Authority / E-E-A-T reports in Lumar can help you ensure that your content is demonstrating signals of expertise, experience, authority, and trustworthiness.
AI Authority, Experience, & Trustworthiness / EEAT Reports in Lumar GEO
| Lumar GEO Report: | What it Measures & Why it Matters for GEO: |
|---|---|
| Pages with Backlinks | This report identifies pages on your site that have at least one backlink. — This report is a foundational indicator of a page’s authority, a key component of E-E-A-T. Backlinks serve as a critical signal that a page has been endorsed by other sources on the web. |
| Indexable Pages with Backlinks | This report shows URLs that have backlinks and are indexable. — This is the ideal state for a page to contribute to E-E-A-T, SEO, and GEO. Backlinks provide authority, and indexability ensures that the authority is not wasted. |
| Disallowed URLs with Backlinks | This report identifies pages with backlinks that are blocked from crawling via disallow directives in robots.txt. — This is a critical issue that harms E-E-A-T, SEO, and GEO. Backlinks are a strong signal of authority, but if they point to a page that is disallowed in robots.txt, crawlers cannot access the content. This means the backlink authority is effectively wasted. |
| Non-Indexable Pages with Backlinks | This report identifies pages with backlinks that have a noindex tag. — Similar to disallowed URLs, this is a severe issue for SEO and GEO alike. Backlinks are pointing to pages that have a noindex tag, meaning the authority of the page cannot be leveraged in the search index. |
| Pages with Backlinks But No Links Out | This report shows pages that have backlinks but do not have any internal or external links on the page. This report highlights a missed opportunity for E-E-A-T, SEO, and GEO. A page with authority (from backlinks) that does not link out is a dead-end for crawlers. This prevents the authority from being passed on to other pages on your site, which is a key part of establishing overall E-E-A-T. For SEO and GEO, this limits the AI’s ability to discover and understand other relevant content on your site. |
| Redirecting URLs with Backlinks | This report identifies pages that have backlinks and also have a redirect. — This highlights a potential performance issue that harms both SEO and GEO. Backlinks are pointing to a page that redirects, which can cause the link equity to be diluted or lost if the redirects are not handled properly (e.g., redirect chains). This could weaken the authority of the final page. |
| Error Pages with Backlinks | This report identifies pages with backlinks that return an availability error (4xx or 5xx). — This is a major issue that completely destroys the value of a backlink for E-E-A-T, SEO, and GEO. Backlinks are pointing to a broken page, meaning the authority is entirely lost. |
| Pages with Meta Nofollow and Backlinks | This report identifies pages that have backlinks but also have a meta nofollow tag. — This is a potential internal linking issue. The nofollow tag on a page tells search engines not to follow any of the links on that page. If a page with backlinks has a nofollow tag, it is not passing its authority on to the internal pages it links to. |
| Empty Pages | This report shows indexable pages with less text content than the ‘Empty Page Threshold’ setting specified in your advanced report settings. — Empty pages may be a bad user experience, increasing bounce and conversion rates. If the pages should not exist, then they will waste crawl budget, which could be used on other, more important pages. |
| Broken Images | This Lumar report shows all images that are linked or embedded on your website but don't return a 200 or a redirect HTTP response. |
| HTTPS Pages | This report shows all pages using the HTTPS scheme. Pages using the HTTPS scheme are more secure and preferred over HTTP. |
| All Broken Links | This report shows all instances of links where the target URL returns a broken status code (400, 404, 410, 500, or 501). — Broken links can result in a bad experience for users if they click the link and arrive at the broken page, resulting in poorer engagement and potential loss of conversions. |
| Unique Broken Links | This report shows instances of links with unique anchor text and target URL, where the target URL returns a 4xx or 5xx status. |
| External Redirects | Shows all internal URLs that redirect to an external URL, outside of the crawl's domain scope. |
| Fast Fetch Time (<1 sec) | Shows all URLs with a fetch time of 1 second or less. — Slow pages can negatively impact crawl efficiency and user experience. This report highlights the pages that load in one second or faster. |
| Duplicate Pages | This report shows indexable pages that share an identical title, description and near identical content with other pages found in the same crawl, excluding the primary page from each set of duplicates. It's likely that the primary duplicate shown is the main version which should be kept. (Canonicalized pages, noindexed pages and pages with reciprocated hreflangs will not be reported as duplicates.) Duplicate pages can result in the dilution of authority signals and reduce the crawl efficiency of the site, wasting crawl budget |
| Duplicate Title Sets | Shows sets of pages that share an identical title tag, excluding pages connected with reciprocal hreflangs. |
| Duplicate Description Sets | Shows sets of pages that share an identical meta description, excluding pages connected with reciprocal hreflangs. |
| Duplicate Body Sets | Sets of pages with similar body content, excluding pages connected with reciprocal hreflangs. |
Semantic Relevancy (Content-Query Relevance) for GEO
AI and traditional search platforms alike don’t just match keywords these days; they use technologies like vector models to understand the meaning and intent behind a user’s query and the content they are attempting to serve in response. This means a page must be contextually and semantically relevant to a topic to be considered a valuable source for the end user.
Semantic Relevance Reports in Lumar GEO
( * = Coming soon )
| Lumar GEO Report: | What it Measures & Why it Matters for GEO: |
|---|---|
| Pages with Search Queries * | This report identifies pages on your site that are being found by users through search queries. — This report is a direct and positive signal for Generative Engine Optimization (GEO). It shows that a page’s content is already semantically relevant and successfully meeting user search intent. |
| Pages with Low / Medium / High Query Relevance * | This report scores how well the content on a page semantically matches the queries that led to it. — This report provides a critical diagnostic for optimizing content for AI. A low relevance score signals a mismatch between the content and what users (and AI bots) are looking for, indicating a need for content refinement. AI systems generally prioritize content that is factually accurate and semantically aligned with the given query, making this report essential for understanding your content’s true effectiveness. |
| Search Queries with Landing Pages * | This report shows which search queries are leading to which landing pages on your site. — By understanding which pages are successfully capturing traffic for which queries, you can gain a deeper understanding of your content’s semantic footprint. |
| Search Queries * | This report shows which specific search queries are leading to which landing pages on your site. — This report is a tracking metric that helps you identify search demand and uncover new opportunities for creating content that is optimized for AI. AI-powered search often responds to long-tail, conversational queries that reveal specific user intent. By analyzing these queries, you can uncover new content gaps and questions that your existing content doesn’t fully address. |
| Pages with Low / Medium / High Title Relevance * | This report scores how well a page’s title semantically matches its corresponding queries. — The page title is a primary signal of a page’s topic and a crucial element for AI’s content understanding. A low title relevance score indicates a disconnect between the title and the content’s actual purpose, which can confuse bots and reduce the content’s perceived authority and relevance to a given query or topic. |
| Pages with Low / Medium / High H1 Relevance * | This report scores how well a page’s H1 tag semantically matches its corresponding queries. — The H1 tag serves as a clear thematic signpost for both human readers and bots. A low H1 relevance score can cause a bot to misinterpret the page’s core topic or perceive the content as disorganized. |
| Pages with Low / Medium / High Description Relevance * | This report scores how well a page’s meta description semantically matches its corresponding queries. |
| Pages with Low / Medium / High Content Relevance * | This report scores how well a page’s main content semantically matches its corresponding queries. — A high content relevance score confirms that your content is doing its job: providing a thorough, in-depth, and semantically rich answer to user questions. |
| Search Queries with Poorly / Moderately / Well Matched Landing Pages * | This report shows the overall success of your pages in matching search queries to landing pages. |
Get started with GEO tools in Lumar
Ready to get started with GEO tools in Lumar?