In this section of our guide to linking, we’ll explain the issues that broken and redirected links can cause for a site, and we’ll also give you best practice advice on how to identify and handle those problem links.
Broken Links
Broken links are internal links to pages that return a 4XX error, such as a 404 error (Page Not Found), which are experienced when a user or search engine lands on a dead link. Server issues, discontinued content or just mistyped links can result in huge volumes of broken links on some sites. This is especially prominent when the links are includes in reused site templates, such as headers and footers.
There are three main elements that can be negatively impacted by broken links:
- Broken links waste crawl budget and send search engines to dead ends within your website’s architecture. The more broken links you have on your site, the more requests bots need to make to dead pages which cuts into valuable crawl budget.
- Pages that have existing good PageRank from high quality backlinks can lose this when the page is repeatedly returned to search engines under a 404 status. This can overall hurt the authority of your site.
- The most obvious impact of a broken link is to user experience. Clicking on dead links is not only frustrating but affects your page and site engagement which not only can affect your crawl budgets for SEO, but also quality scores across paid traffic channels.
How to Identify & Fix Broken Links
The best way to fix broken links is to change them at the source rather than implementing a redirect on the destination URL. Here’s how to identify broken link issues:
- Crawl the site using your favourite crawling tool such as Lumar, Screaming Frog etc.
- Review the following reports:
- Google Search Console ‘crawl errors’ report
- Bing Webmaster Tools ‘crawl errors’ report
- Yandex Webmaster ‘HTTP status: not found (404) report
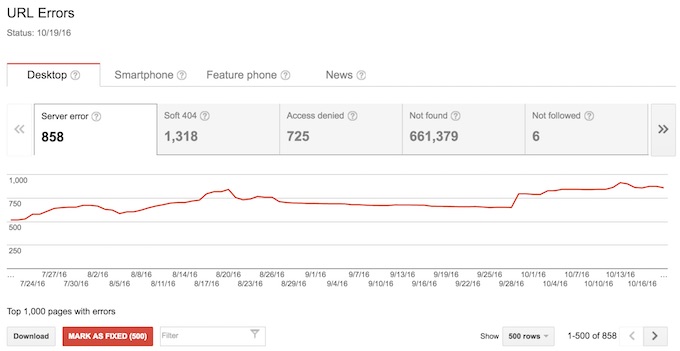
Image source: www.rebelytics.com/crawl-errors-google-search-console/
- Check your analytics platform to see if HTTP status codes are being recorded, and examine any 40X instances
- Analyse your log files to find the 404 pages that users and search engines are landing on
Now that you’ve compiled a list of error pages, here’s how you can fix broken link issues:
- Update 404 pages at the source, for example update the URL hyperlink
- Remove the error page from the source page if it has truly been removed
- If the 404 pages happen to be an entire directory or bulk section of pages and updating the links manually is not possible, here are some redirection methods (although redirection when it comes to broken links is not recommended, which we’ll cover in the next section of this guide):
- Update the .htaccess file or NGINX server config to create bulk redirects
- If you use WordPress, many redirection plugins are available
You should ensure you are checking for broken links consistently, or at least at regular intervals, as they can be easily fixed and impact SEO performance.
Redirecting links
Redirecting links are links which point to pages with 301, 302 or any other 3XX HTTP status codes, as well as META refreshes. This also includes links with redirection chains.
Here are the different ways in which redirecting links can negatively impact a website:
- Crawl budget is wasted as search engines must crawl the URLs which redirect to be able to find the destination URLs.
- Some PageRank may not be passed through 301 redirects. In 2013, Matt Cutts indicated that that 301 redirects only pass 85% of pagerank and that 15% of pagerank is lost. More recently, Gary Illyes tweeted that “30X redirects don’t lose pagerank anymore.” PageRank is only one of many ranking signals, so don’t rely on Google to pass on everything and keep site architecture as clean as possible. Also, keep in mind that Google is not the only search engine and all redirects have historically come with link equity loss baggage.
- PageRank isn’t passed through 302 redirects as these are temporary and are, therefore, treated by search engines differently than permanent redirects. However, if a page consistently 302 redirects to a destination URL for a long time, the redirect may be treated as a permanent URL.
- Some PageRank is lost through meta refresh so it is highly recommended that these are not used as they can impact usability.
- Redirects negatively impact user experience because the user undergoes a wait while the redirection takes place. This can lead to increased bounce rates especially on sites with heavy mobile and tablet usage, because users on mobiles tend to have slower connections and higher latency than those on desktop machines.
It’s important to note that in the case of HTTP to HTTPS 301 or 302 redirects do not cause any loss in PageRank, as confirmed by Google.
How to Identify & Fix Redirecting Links
Similar to the solution for fixing broken links, the best way to fix redirecting links is to change them at the source. Here’s how to identify redirecting link issues:
- Run a crawl of your site using a crawling tool such as Lumar, Screaming Frog etc.
- Check your analytics platform to see if HTTP status codes are being recorded, and examine any 30X instances
- Obtain a list of any current server-side redirects by looking at log files, for example
Now you’ve compiled a list of internal redirects on your site, here’s how to fix redirecting link issues:
- Update target links on source pages. Ensure they are pointing to the final destination page avoiding all redirects.





