Websites evolve over time, undergoing changes including migrations, site architecture alterations and content consolidation to name a few. When SEOs are tasked with implementing these types of changes, redirection is often a crucial process by which site visitors and search engine crawlers are automatically directed to the correct version of a page.
In this section of the Technical SEO Library, we’ll dig into what redirection is, how it works and each of the different types of redirects.
What are URL redirects?
URL redirection is the automatic process of forwarding a client from the requested URL to a target URL. Redirection can be implemented in a number of ways, and can be added either permanently or temporarily. A redirect is considered to be complete when the user has successfully been sent to the destination URL.

How does URL redirection work?
When a server wants the user to be sent to a different page than the one they requested, an HTTP status code of 3xx is passed along with a ‘location’ header (which contains the intended target URL).
An example HTTP/1.1 response header for a 301 redirect looks like this:
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
Location: https://www.example.com/
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 150
Redirect chains
What is a redirect chain?
A redirect chain occurs when there is more than one redirect between the initial URL and the destination URL.
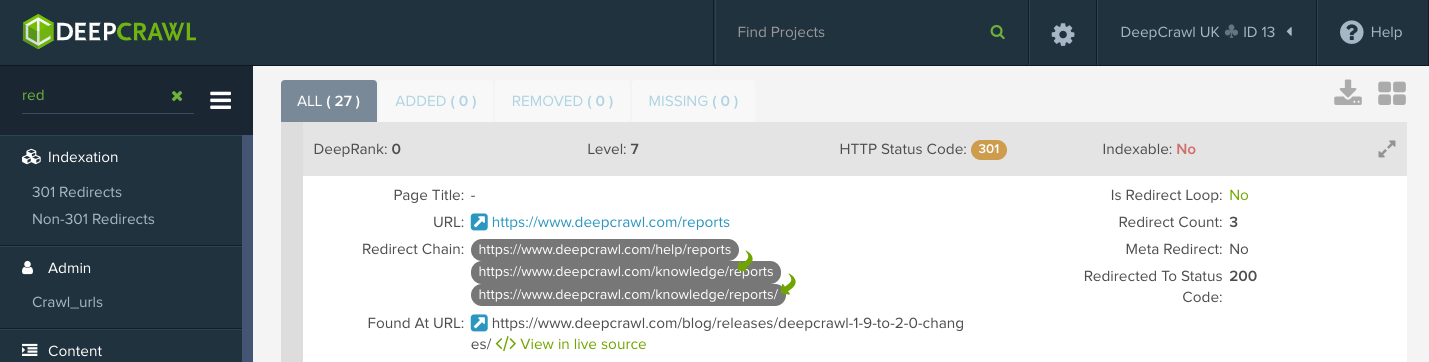
Why do redirect chains occur?
Most redirect chains occur inadvertently. The most common example is when URL X is redirected to URL Y, and after a period of time URL Y is redirected to URL Z.
Another example is a combination of non-www vs www, and HTTP and HTTPS URLs resulting in sitewide redirect issues. For example, the non-www HTTP version redirects to the www HTTP version which redirects to the www HTTPS version (https://example.com > https://www.example.com > https://www.example.com).
How do redirect chains impact search engines and users?
While redirect chains may occur naturally, they do impact user experience and crawl budget. As each redirect request to the server needs to be processed and answered, latency is increased with each request, leading to a slower user experience. After a number of server requests, users will also receive a “too many redirects” error warning once the redirect limit has been reached.
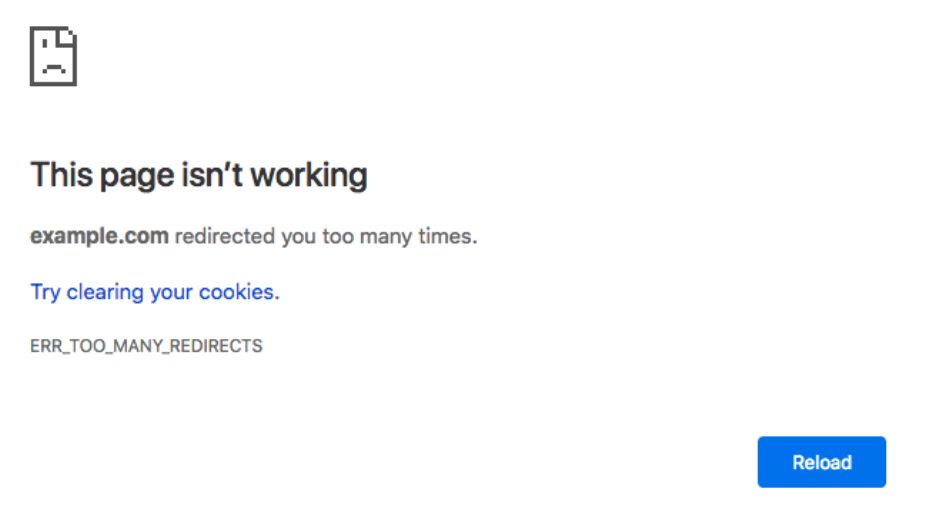
With regards to how search engines treat redirect chains, it is important to consider that:
Redirect chains may not impact PageRank, but search engines may stop following redirect chains after a certain amount of redirects. For example, Google follows a maximum of 5 redirects.
Any disallowed URLs in a redirect chain stop it from being followed.
Internal links should try to avoid pointing to redirecting URLs, as this will have an effect on crawl budget.
How do redirects impact crawl budget?
Each redirect causes search engines to issue another request to find the destination URL. This means that the more redirects implemented in a row or across a website, the greater impact this will have on crawl budget.
If the majority of a website’s crawl budget is taken up by redirects, priority pages on your website will be crawled less often, or not at all. This can also lead to a longer time being taken for a full crawl of the site, which will reduce the freshness of the website’s pages in a search engine’s index.
Redirect loops
What is a redirect loop?
A redirect loop occurs when a page ends up redirecting back to itself, possibly via other pages, which in turn leads to an infinite number of redirects.
Why do redirect loops occur?
Redirect loops can happen due to temporary cacheable redirects. For example, when a non-www URL redirects to www URL, and the redirect is cached, but then this is reversed.
Also, If a user visited the URL before it was reversed, and then returns afterward, the user may see the redirect back to the original URL and cache that as well. This would result in a loop between the two URLs.
How to detect redirect chains and loops
The best way to detect redirect loops at scale is by using a crawler. After crawling a site with Lumar, our platform reports on all instances of redirect chains and redirect loops in separate reports. On top of this, you can track the total number of instances of redirect chains and loops from crawl to crawl to monitor this on an ongoing basis.
You can find out more about dealing with redirecting links in our section on handling broken & redirecting links.
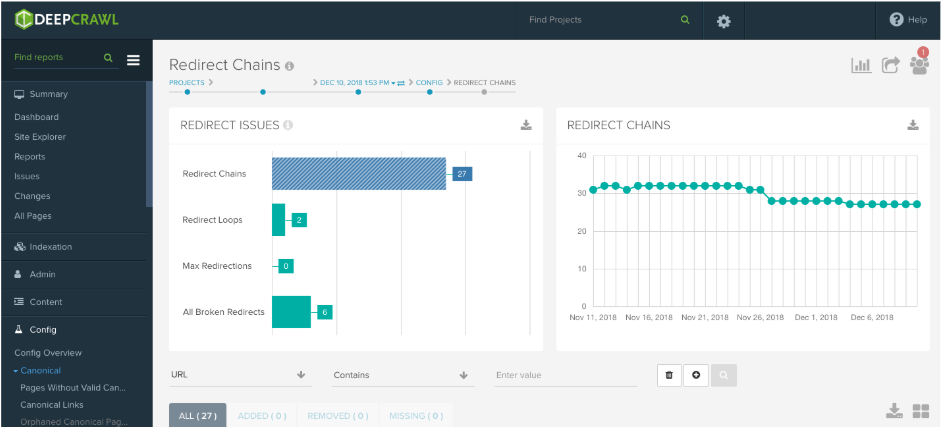
Start detecting redirect issues now
If you’re interested in finding out if your site has redirect issues, you can get started with Lumar’s website intelligence platform now and start discovering redirect chains and loops that could be negatively impacting your site.







