BrightonSEO was back with a vengeance last Friday – it was bigger and better than ever. As always, the day was littered with a host of top speakers eager to share their unique insights on all things search.
The DeepCrawl team were out in full force, taking over the East bar with retro arcade games and free beer (as per usual!) A special shout out goes to everyone that took to the stage for the DeepCrawl Karaoke Pre-Party, there were some truly memorable performances that will live long in all of our memories!
Watch #BrightonSEO up this morning. Catch our talk about creating video cheap and fast…We are last on in Meeting Room 1 @brightonseo #mobilevideo #videocontent pic.twitter.com/ckMELRu9k7
— Touch Video Academy (@TouchVideoAcad) April 27, 2018
Rob Bucci – Featured snippets: From then to now, volatility, and voice search
Talk Summary
Being the SERP stalkers that they are, STAT have studied featured snippets extensively and their founder, Rob, did an excellent job of communicating their findings in Auditorium 2. Even if you aren’t particularly interested in featured snippets, for whatever reason, it’s worth flicking through Rob’s deck, as you won’t find many that are better designed. Speakers, take note.
Key Takeaways
The Research
STAT have researched the behaviour of featured snippets, studying 4 million of them as part of their latest white paper.
As well as looking at the prevalence of featured snippets in the SERPs, the STAT team wanted to investigate how frequently they change (volatility) and what other search features they are displayed with (co-occurrence) to determine if targeting featured snippets is a stable strategy for SEOs.
What did they find out about featured snippets?
31% of the keywords included in the research had a featured snippet. Compared to their previous measurements, STAT are seeing featured snippets become increasingly prevalent over time.
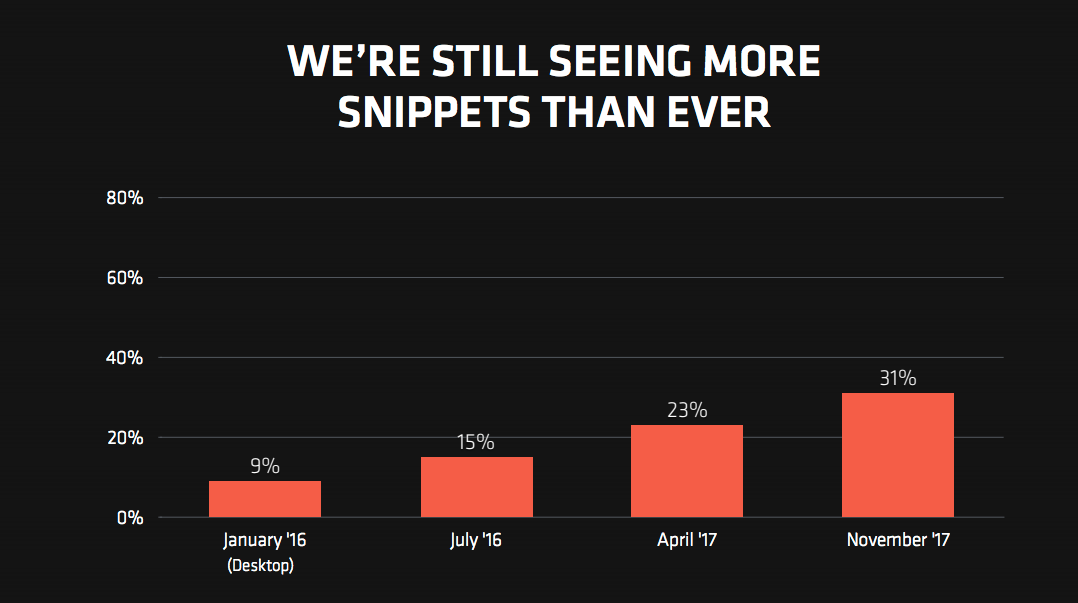
Featured snippets are at the top of the results they appear in 96% of the time. They appear second place when they are displayed alongside shopping boxes.
Having your page shown as a featured snippet enables you to leapfrog other results even if the actual result is ranked lower.
Since their original research, STAT have found the organic rank of the page included as a featured snippet has dropped from an average position of 2 to 3 – lower ranking results are being used as featured snippets more frequently.
However, having a higher ranking page is still going to increase the likelihood that it will appear as a featured snippet. 99% of snippets are sourced from ranks 2-10.
What SERP features co-occur with featured snippets?
When a featured snippet is present, a “People Also Ask” box is in second place 60% of the time.
Featured snippets co-occur with images 7% of the time, shopping 4% of the time and with News and Places 1% of the time.
Video results are growing in prevalence and in co-occurrence with featured snippets. If you are working with an authoritative site that can answer questions with video, then this could be a big win.
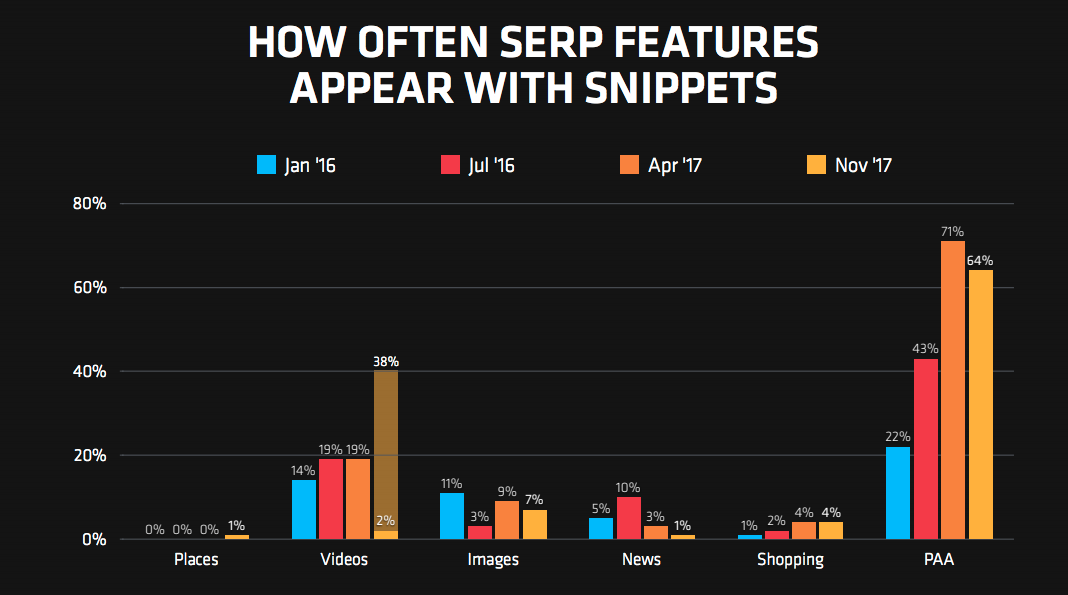
Rob encourages you to let “People Also Ask” boxes to inspire your snippet content. Build out your query universe from root queries and make sure that your site is answering these questions.
The research found that snippets used to rarely co-occur with places, but this is starting to change.
This co-occurrence happens when Google is trying to satisfy ambiguous intent.
For example, searching for “top casinos” could be about finding a physical or online casino so Google caters for both intents.
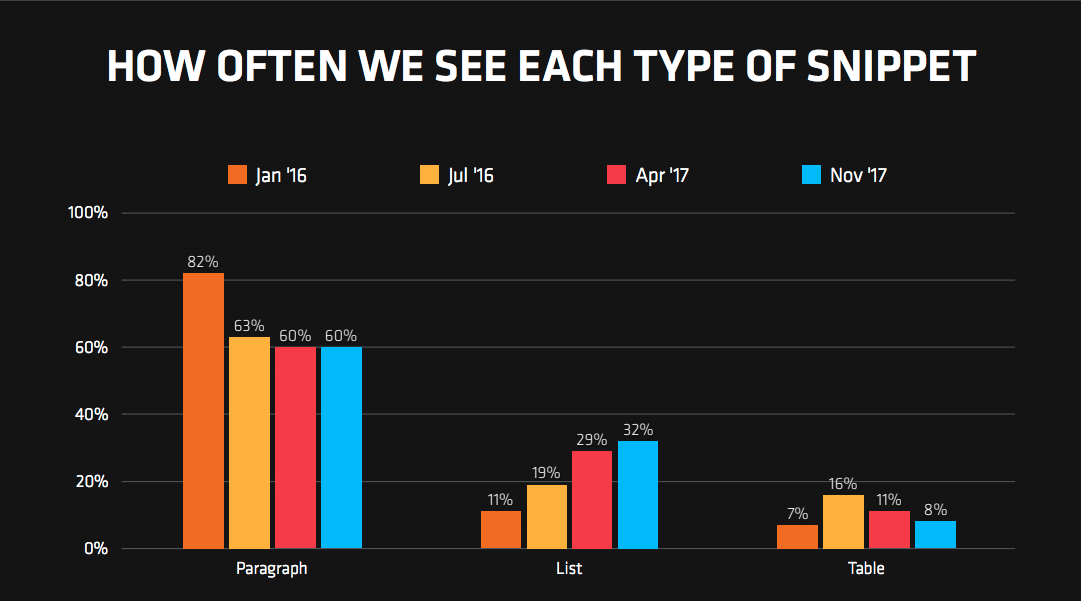
How are featured snippets formatted?
Featured snippets are most commonly formatted as paragraphs (60% of occurrences), followed by lists and then tables (32% and 8% respectively).
However, paragraphs and tables are declining in the overall proportion of occurrences and lists are on the rise.
Queries including “Best” and “How to” queries are most common for list snippets.
How volatile are featured snippets?
Volatility is defined by disappearances, reappearances or URL changes of featured snippets. Volatility was tracked over a 20 day period.
- 68% of featured snippets showed zero volatility.
- Health queries with featured snippets showed the highest amount of volatility.
- Most common cause of volatility is a URL changing. When this happens Google shops round for better content to populate featured snippets.
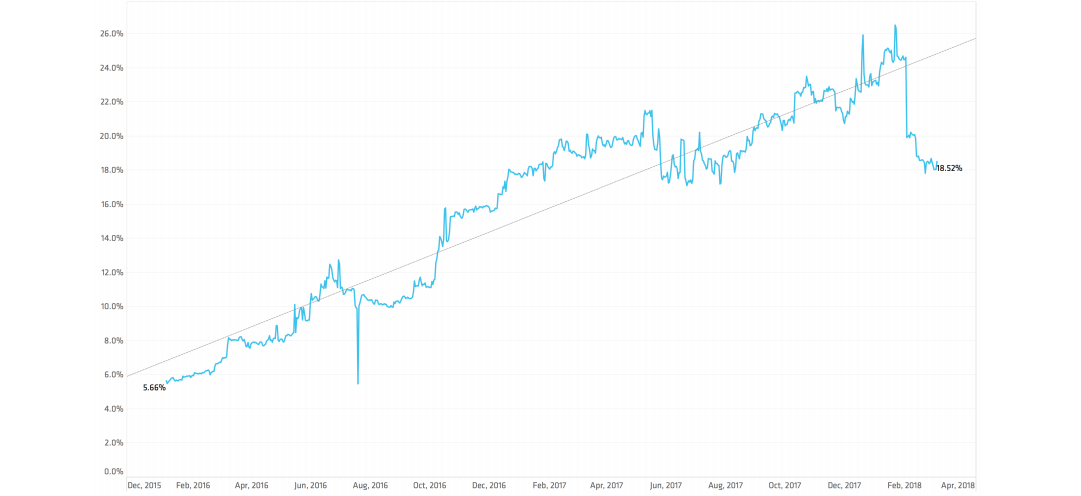
Featured snippets and voice search
Google Assistant relies on featured snippets for answers.
Natural language is becoming more important. Google is expanding types of queries that snippets are used for.
Full sentences are triggering featured snippets more and more as seen in the graph below.
From Black Friday to iPhones – how to rank for big terms on big days – Sam Robson
Talk Summary
Sam provided some excellent enterprise insights from the challenges he has faced in his role as Director of Audience at Future Publishing. Sam’s talk showed how setbacks caused by algorithm updates and a changing search landscape can be turned around using examples from first-hand experience.
Key Takeaways
A Baptism By Fire
Sam has worked at Future Publishing for a number of years and the combined traffic from their sites totals 62 million monthly users.
- Their largest site, TechRadar, ranks well for many high volume queries around Black Friday, phone releases and any technology searches featuring “Best”.
- A week after Sam joined Future Publishing, Google’s Panda update was released and TechRadar lost 50% of its traffic.
- Many technology sites didn’t recover but within four months of the algorithm update TechRadar recovered and had actually increased traffic by a third compared to before Panda.
- Google’s Panda update forced Sam and the team to be better.
Sam overcame the site’s issues by addressing pages that offered a bad user experience and were poor quality. Sam says it’s crucial that all of a site’s pages are spot on, not just a proportion of them.
The Importance of Technical SEO
Technical SEO is more important than ever and Google now recognises need for SEOs.
- Techradar had issues with errors due to lack of maintenance – error creep and traffic issues.
- These issues were fixed and traffic improved as a result.
- TechRadar got a boost after Fred update because they were better than competitors.
An elite domain is going to allow you to rank for elite terms and give you access to an elite audience.
Redirect chains and broken pages are important issues that make a difference and need to be fixed.
- Pay attention to Search Console as this will diagnose these problems.
- However, you need a specialist crawler for enterprise sites like TechRadar, as these allow you to go beyond the 1,000 row limit in Search Console.
Expert Insights For SEOs Working For Large Publishers
Tidy up your archives. These older pages need to stand up to 2018 standards. Noindex them or get rid of them if you can’t improve them.
Links are less important than they were. Sam has seen evidence of TechRadar publishing articles that rank 1st without links because of the authoritativeness of the domain.
Sam has seen that speed and good user experience are especially important for ranking on mobile even before mobile-first indexing started to roll out.
TechRadar’s strategy involves proactively publishing on future phone releases, as they can predict when they are likely to be released and searched for e.g. iPhone 11 – What we want to see.
Sam has also found a way for limiting SERP fluctuations after a release when the competition grows with more being written about the release in question.
Sam stressed the importance of picking your battles carefully as there may be some terms which you are highly unlikely to rank for.
- Search volume isn’t always the best indicator of what you should try and rank for, consider searcher intent as well.
- Diversify the keywords you want to rank for but avoid cannibalisation.
TechRadar’s traffic has shifted to a mobile majority in a relatively short amount of time.
- Mobile traffic now accounts for 70% of TechRadar’s traffic and this has been driven by newly added carousels in mobile search.
- Presence in these carousels is driven by domain authority, relevance and technical proficiency of the site.
- AMP and video now gives sites the possibility of getting a site included four times on page 1.
A Universal Strategy for Answer Engine Optimisation (beyond position 0) – Jason Barnard
Talk Summary
Jason rounded off what was an excellent session in Auditorium 2 with a more philosophical talk covering how Google is using Machine Learning and how you should form a strategy around ensuring answer engines understand what your site/brand is about, reinforcing these with credible signals.
Key Takeaways
Google is now an AI company and their search engine has become an answer engine which we need to understand the inner workings of so we can form a strategy.
The Landscape
Voice assistants are becoming the norm and when we’re looking at optimising for them we need to consider that there are two sides to the equation.
- The front end is all about understanding the user and intent.
- The back end is all about providing an answer.
Machine Learning
Google have appointed veteran engineers and there has been a big “AI-first” push within the company.
Machine learning is starting to run search algorithms on the front and back end and there are three types:
- Supervised – Where the rules are known
- Unsupervised – Where no rules are known
- Semi-supervised – Where some rules are known
RankBrain is generally associated with the front end, but it doesn’t just understand user intent (understanding the question). RankBrain also helps Google to understand the available options (providing the answer).
The Strategy
Google is moving away from the knowledge graph with full information manually inputted. Google will eventually allow machine learning more freedom to deduce nodes from search queries as well as attributes.
As a result, you should make sure you communicate to Google who you are and what you offer with clear unambiguous content.
Corroboration – Provide Google with social proof and consistent signals that allow them to have more confidence in their understanding.
- Google is training machines to learn to learn and SEOs need to help them.
Pick four platforms and get positive reviews going e.g. trustpilot. Use your brand name plus ‘reviews’ to find the top four review platforms relevant to your business. - Despite popular belief you don’t need a Wikipedia page to appear in the knowledge panel.
- Create a positive buzz around your brand.
Why Brand is Replacing Authority – Ade Lewis
Talk Summary
Ade’s talk on the growing importance of brand provided a good overview of what it means to build a brand and how this is gradually becoming a ranking factor.
Key Takeaways
Old School Google
Ranking in Google used to be about relevancy and authority, where the former took into account everything that was written on a website and how relevant it was to a given search term and the latter being anything written about you on external sites (AKA external links).
The problem with Google’s “old school” reliance on authority is that it left them open to manipulation with paid links.
Google has gotten increasingly better at detecting deceptive link behaviour, like paid links. Tom Anthony has a useful article on how to detect anomalous linking activity.
Google has had to evolve
Google has had to evolve to look at non-link based signals – algorithm updates like Penguin have been part of this.
However, there is still an issue because while Google is trying to move away from authority as a ranking factor, we are still fundamentally focused on building authority. This is still the main intent behind content marketing and digital PR.
The power of brand and why it matters
Brand is the personality of a business and its reputation. A brand is the sum of all customer experiences with a company and is therefore defined by customers and not by the business itself.
- Every interaction someone has with your business shapes your brand.
- If digital marketing is the solar system, then brand is the galaxy.
- A good brand is based on personal experience and knowing, liking and trusting the source.
- This is the same for Google, except they don’t have the luxury of personal experience. Instead Google has to rely on proxies like reviews, brand searches, engagement metrics.
- Links are becoming less effective unless they are backed by strong brand signals.
- Think about it this way, do people leave reviews and talk about a brand because it has backlinks? Or is it more the case that a brand earns links because people are talking about the brand and leaving reviews as well as knowing, liking and trusting it?
Ade had a great slide on the brand signals which Google take notice of:
Companies need to think about their brand values. Ade has written a great article on the components of brand value.
- Brand values are similar to an iceberg because most of these aren’t externally visible.
- What can be seen: company behaviour, identity, personality, voice, brand signals
- What can’t be seen: knowledge, experience values
- Make sure your company has a set of defined values that fully represent your ethos.
- Ensure the people running campaigns and writing your content understand your brand values.
- Only pursue coverage on sites that align with your brand values.
Ade asked a few industry experts what a brand is and Greg Gifford defined it as:
“It’s what gives people warm fuzzies or makes them throw up in their mouth a little bit when they hear the name of the company.”
Final thoughts
Links are not dead, they are now brand signals.
Don’t give up on content marketing and digital PR, just make sure they fully align with your brand.
Focus on building brand signals that correlate with good rankings.
Killing Giants – How to compete with Big Brands in the SERPS – Ross Tavendale
Talk Summary
Ross’ humour-filled talk revealed a ton of smart tactics that he and the team at Type A Media use to compete with big brands with limited time and resource.
Key Takeaways
Being efficient with your time
Killing giant competitors is all about doing the same as them, but working faster and more efficiently.
Ross ran a Twitter poll asking people how long a 1,000 page technical audit typically takes. 60% said one week and 20% one month. One person even said that an audit shouldn’t take less than a month.
- Ross thinks this is really slow. His message: pull your finger out!
- Ross recommends installing Rescue Time to see how little work you actually do.
Ross is all about finding efficiency hacks. He bought his team Bose Noise Cancelling headphones and productivity went up by 50% according to Slack activity.
- Alternatively, you could consider deleting Slack altogether.
Kill giants by achieving perfect technical SEO.
- Think about how many surprises you get each and every month.
- Being able to monitor changes in the basics (e.g. SSL and canonicals) can make a huge difference and save you a lot of time.
- Lock it down by using Little Warden to monitor the tedious.
- Consider using Content King to get a running list of the changes made to a site.
- For larger sites run crawls using DeepCrawl so you are always working with fresh data. Ross and his team crawl sites 3 times per week.
Fix broken stuff – 404s, orphans and non-indexed pages
- Find them and fix them quickly.
- Finding all the URLs that have ever existed on a site can take hours if you’re populating Google Sheets with data from archive.org, Analytics, Search Console and Majestic and then deduplicating them.
- Ross has a handy Python script that allows you to do this in just 60 seconds.
Orphans and weak pages
- Improve internal linking by linking to big commercial brand pages to release pockets of power.
- Mapping keywords to URLs manually would involve running a site: query, running a custom search within a crawler to understand internal linking, using ScrapeBox to find the URLs which rank for each keyword, processing 10 at a time.
- Ross also has a python script that reduces this 4 hour process down to 60 seconds.
Identifying content gaps
- Finding gaps in a site’s content is about figuring out what pages you need and establishing what they should look like
- This involves pulling all marketplace keywords, categorising them effectively, identifying high and low opportunity and comparing them against the site’s existing pages to find the gaps
- Doing this in AdWords is slow!
- Your secret weapon is in using Supermetrics, SEMrush and Google Sheets. Ross has a template which helps speed up this process.
Going after big links
Only build links with bragging rights attached to them.
Consider the algorithmic vs. flop risk.
- A PBN link carries a high algorithmic risk as it is spammy but a low flop risk because you know you definitely get that link by adding it yourself.
- A link on a national news site carries a low algorithmic risk because it is from a highly reputable source, but a high flop risk because they are hard to obtain.
Ross has a few recommendations for coming up with data-led stories.
- Stop building massive lists, don’t make it too difficult to verify.
- Keep it niche, syndication is your friend and use your initial success in your favour.
- Get the mention first and then ask for the link back. Ross has learned that you should ask the IT managers at major publishers to add links as the journalists aren’t responsible for this.
- Fresh angles on pop topics are good bets for getting decent coverage as they are easily verifiable.
Preemptive Reputation Management – Julia Logan
Talk Summary
Julia finished the last speaking slot of the day before the keynote with a useful talk about the importance of pre-emptive reputation management and how it can be successfully incorporated into a company’s existing brand-building activities.
Key Takeaways
Brand building and image
- Brand building is tightly connected with creating a message and is about influencing how people perceive your brand. Brand building is also closely aligned with reputation management.
- Brand image and reputation comes from many different sources like social media, third party mentions and search.
Additional search features are a potential risk for brands
- Online reputation disasters can happen to anyone.
- Google now has many different features in search like knowledge panels, search suggestions, related searches, “People Also Ask” boxes, short click boxes etc.
- Each of these additional search features is an additional element that could be a potential banana skin for brand to slip up on.
- Negative search suggestions are going to lead to negative content about your brand e.g. searching for “volkswagen emissions” will provide suggestions relating to the VW emissions scandal.
Mending a brand’s reputation
- It’s not impossible to fix a brand’s reputation after a disaster but fixing bad reputation takes a long time.
- There’s no guarantee that a brand’s reputation will ever be fixed and it can be a painful and complicated process.
How can you fix something bad that starts ranking organically for your brand?
- Negative SEO is a poor option because it can be easily traced and can do even further damage to the brand.
- Trying to outrank the offending content is another option but can take a long time and a lot of resources as it is likely to require a lot of positive exposure.
- If a brand has already received negative exposure then you have no choice but to react to it but if it hasn’t then pre-emptive reputation management is a good strategy to consider.
Benefits of pre-emptive reputation management
Pre-emptive reputation management saves in the long term and can be incorporated into a brand’s existing activities.
How do you go about pre-emptive reputation management? Be prepared and ensure your brand receives plenty of positive exposure for the message you are attempting to get across.
If you’re not just trying to get positive exposure at the time of crisis then it’s going to make your brand more resistant to any negative exposure that might come your way in the future.
Don’t forget that every positive mention counts and to use multiple channels to put out your message to reach more people.
Try to encourage people to search for your brand in the desired content and be creative about it – do something your competitor won’t.
Ultimately, investing in pre-emptive reputation management is going to result in a better brand image.





